The questions on this free Mechanical Reasoning practice test are a true representation of the questions you'll face on the actual Mechanical Reasoning Aptitude Test.
These Mechanical Reasoning sample questions were specifically chosen from our full Mechanical Reasoning test practice pack to help improve your score and ace your pre-employment process.
Free Mechanical Reasoning Practice Questions
Sample Question 1
1. Which bird will find it easier to fly?
Answer:
The correct answer is (A).
Explanation:
The bird in picture A flies with her wings backward, minimizing the contact surface with the wind and creating less resistance. The bird in picture B flies with her wings in the wind direction, creating much more resistance. The same phenomenon makes a crumpled piece of paper fall faster than an open sheet of paper, which has more surface and more resistance.
Remember the physical principle: The larger the surface of contact with air/wind, the more resistance (force) is created.
A mechanical reasoning test is an aptitude test administered as part of the recruitment process for technical positions. These tests assess your ability to grasp mechanical concepts and apply them to resolve problems. Get a better understanding of what to expect on the Mechanical Reasoning Assessment Test by practising for the test.
Other preparations which include Mechanical Reasoning practice tests: SHL, Ramsay, Bennet.
Sample Question 2
2. In which direction should the acrobat move his body to balance the seesaw?
Answer:
The correct answer is B.
Explanation:
A seesaw is an example of a first-class lever, where the fulcrum is between the effort and load. For the seesaw to be balanced, the torque applied by the acrobat must increase. Since the acrobat's weight is constant, the only way to increase the input torque is by increasing the distance from the fulcrum.
Moving in direction B will shift the acrobat’s centre of gravity farther from the fulcrum, resulting in greater torque, thereby balancing it.
Sample Question 3
3. Which way is the wagon accelerating?
Answer:
The correct answer is A.
Explanation:
The pendulum is moving backward; therefore, the car is accelerating in the opposite direction. What happens when an object is in an accelerating system, in the same way, you feel pulled back when the car is speeding up or forwards when it is braking.
Remember the physical principle: When an object is within an accelerating system (another object that accelerates or decelerates), the inner object's force will be in the direction opposite to the acceleration.
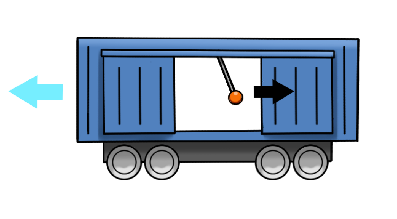
Note: Deceleration is considered a backwards acceleration.
It is common to use mechanical reasoning assessments as a qualification tool in a variety of fields and industries. Any position that entails maintaining, operating, or repairing mechanical equipment falls into this category. Depending on the mechanical skills required, these tests vary in difficulty and need accurate and specific preparation. Other preparations which include Mechanical Reasoning practice tests: SHL, Ramsay, Bennet.
Sample Question 4
4. Which pendulum will swing faster?
Answer:
The correct answer is A.
Explanation:
Pendulum A has a shorter string; therefore, it will swing faster.
Intuitively, the shorter pendulum has less distance to travel in every cycle and, therefore, will move faster.
The bob's mass is irrelevant since the pendulum is affected by gravity, which applies the same acceleration on each body, regardless of its mass. Both bobs accelerate the same; therefore, their mass does not affect the pendulum’s movement.
Remember the physical principle: The only thing that determines how fast a pendulum will swing is its string length.
Sample Question 5
5. In which direction does the grey wheel turn?
Answer:
The correct answer is A.
Explanation:
When contact is made between the rack (toothed belt) and the cogwheels, a conversion from a linear velocity to an angular momentum occurs. The location of the point of contact is critical.
The point of contact between the red cogwheel and the rack is in the lower part of the red cogwheel. The counterclockwise angular velocity induces a linear velocity to the right.
The point of contact between the grey cogwheel and the rack is in the upper part of the grey cogwheel. The linear velocity to the right (determined by the rack) induces an angular momentum in a clockwise direction. The blue arrow shows how each part of the wheel is moving under the rotation conditions:
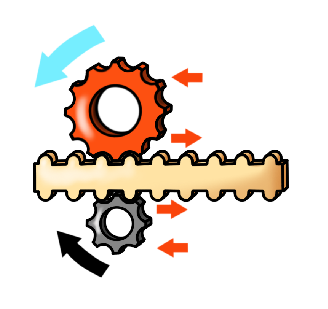
Remember the physical principle: When converting the linear velocity of a rack to the angular momentum, “translate” the rotation into arrows and follow the directions.
Practising Mechanical Reasoning preparation questions will help you gain a better understanding and ability to apply mechanical and electrical principles such as Gears, Pulleys and Everything in Between correctly will boost your chances of landing the job you want.
Sample Question 6
6. Which granary can hold more wheat?
Answer:
The correct answer is C.
Explanation:
This question can be solved in a straightforward calculation of the volume of the granaries, using the formula of a cylinder’s volume:
V = π x R2 x H
Π = 3.14, R is the cylinder’s radius, and H is the height of the cylinder.
Calculating:
Answer A: 4 x π x 52 x 10 = 4 x π x 25 x 10 = 3.14 x 100 x 10 = 3,140
Answer B: π x 52 x 40 = π x 25 x 40 = 3.14 x 1,000 = 3,140
However, there is no need for such lengthy calculations. As we can see, the height of the cylinder affects the volume of a cylinder linearly, meaning four cylinders with height H are equal in volume to one cylinder with height 4H:
V (4 short) =4 x {π x R2 x H} = 4 x π x R2 x H
V (1 tall) = π x R2 x 4H = 4 x π x R2 x H
Remember the physical principle: The volume of a cylinder is linearly dependent on its height.
Note: The same does NOT apply to the cylinder’s radius since the R in the formula is squared. In that case, the volume of one cylinder with a radius of 2R will be equal to the volume of four cylinders with a radius R. The volume of one cylinder with a radius of 4R will be similar to the volume of sixteen cylinders with a radius R.
Sample Question 7
7. In which direction will the wheel spin?
Answer:
The correct answer is B.
Explanation:
A band connects the two wheels on the left; therefore, the top's wheel will spin counter-clockwise. The two wheels at the top are connected by a rod; thus, both rotate in the same direction. The wheel in question is connected by a band to the top right wheel and influenced by its rotation.
Passing this test will lead to an invitation to the assessment centre. As a final step, you will be required to complete a supervised Mechanical Comprehension Test. Practice Mechanical Reasoning test questions and give yourself an advantage over other candidates.
Sample Question 8
8. Who will need to apply more force to lift the weight? (If equal, Mark C.)
Answer:
The correct answer is C.
Explanation:
The figure in B has a wheel to reel in the rope. However, this wheel does nothing to divide the force and only changes the pulling from a linear motion in A to a circular motion in B.
Remember the physical principle: In a pulley system, the wheels that reduce applied force are supporting wheels, not wheels that only change the motion’s direction.
Sample Question 9
9. Which ball will reach the floor first? (If equal, Mark C.)
Answer:
The correct answer is C.
Explanation:
Gravity is applied to both balls equally, and the vertical distance they ought to pass is identical. The time needed for both balls to hit the ground is similar, regardless of the horizontal velocity component.
Therefore, it can be deduced that both balls will hit the ground at the same time.
Remember the physical principle: When an object falls under gravity's influence, its vertical velocity does not depend on the horizontal velocity
Practice is crucial if you want to increase your chance of passing the assessment centre screening. JobTestPrep offers an All-Inclusive preparation pack with full answers and explanations. Other preparations which include Mechanical Reasoning practice tests: SHL, Ramsay, Bennet.
Sample Question 10
10. Which of the three following diagrams is correct?
Answer:
The correct answer is A.
Explanation:
The bending of the partition is caused by pressure difference on both its sides. The level of water determines the pressure difference in each container.
The height of water determines the pressure on the container – the higher the water – the greater the pressure.
In A, the partition bends to the right, suggesting the pressure is greater on the left side. That is consistent with the higher water level on the left side.
In B, the partition is flat, suggesting no pressure difference between its two sides, despite the different water levels. Therefore, this answer is false.
In C, the partition bends to the left, suggesting the pressure is greater on the right side. That contradicts the higher water level on the left side. Therefore, this answer is also false.
Remember the physical principle: Higher water level – higher pressure.
Answer Index
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| A | B | A | A | A |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| C | B | C | C | A |
Continue Practicing for the Mechanical Reasoning Exam
Access more Mechanical Reasoning practice tests and other valuable Mechanical Reasoning prep materials so that you take the test while being as prepared as possible:
- All-Inclusive Mechanical Reasoning - 21 Mechanical and Electrical aptitude practice tests, 12 Spatial Reasoning tests, and 6 Ramsay Institute-style practice tests.
- SHL Mechanical Comprehension Test Practice - 4 full-length SHL Mechanical mock tests (72 questions total) and 21 additional mechanical practice tests (segmented by topic).
- Free SHL practice Test - including Mechanical Reasoning.
- Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test (BMCT) Practice Test - Includes Full BMCT-I and BMCT-II Practice Tests as well as 21 more Mechanical Aptitude Practice Tests.
- Ramsay-Style All-Inclusive - 21 Mechanical Aptitude Practice Tests + Additional Drills.
- Aptitude Tests for Graduates, Managers & Professionals - 11 Mechanical Reasoning tests and 58 Numerical Reasoning, 30 verbal reasoning, 61 abstract, inductive, spatial and diagrammatic reasoning tests.
Create Your Custom Assessment Prep Kit
Job-seeking can be a long and frustrating process, often taking months and involving numerous pre-employment tests and interviews. To guide you through it, we offer a Premium Membership.
Choose 3 Preparation Packs at 50% discount for 1, 3, or 6 months.
More Free Practice
We at JobTestPrep find the assessment tests world highly diverse and fascinating. If you are looking to deepen your knowledge in the aptitude tests world, or you want some extra practice before your test, we've got you covered!
Check out these fantastic free practice tests (all are completely free):
Free Aptitude Test | Free Psychometric Test | Free Numerical Reasoning Test | Free Verbal Reasoning Test | Free Cognitive Test | Free Critical Thinking Test | Free Abstract Reasoning Test | Free Spatial Reasoning Tets | Free Personality Test | Free Inductive Test | Free Mechanical Reasoning Test




